Local Names:
Northern Provinces: หอมด่วนหูเสือ หอมด่วนหลวง (haawm duaan huu seuua, haawm duaan luaang). Issan: เนียมหูเสือ (niiam huu seuua). Shan: ผักฮ่านใหญ่ (phak haan yai). Central Plains: ผักหูเสือ (phak huu seuua).
Common names: Cuban oregano, Country borage, French thyme, Indian borage, Indian mint, Mexican mint, Orégano francés, Soup mint, Spanish thyme, Thick leaf thyme or broad leaf thyme. [1]Wikipedia
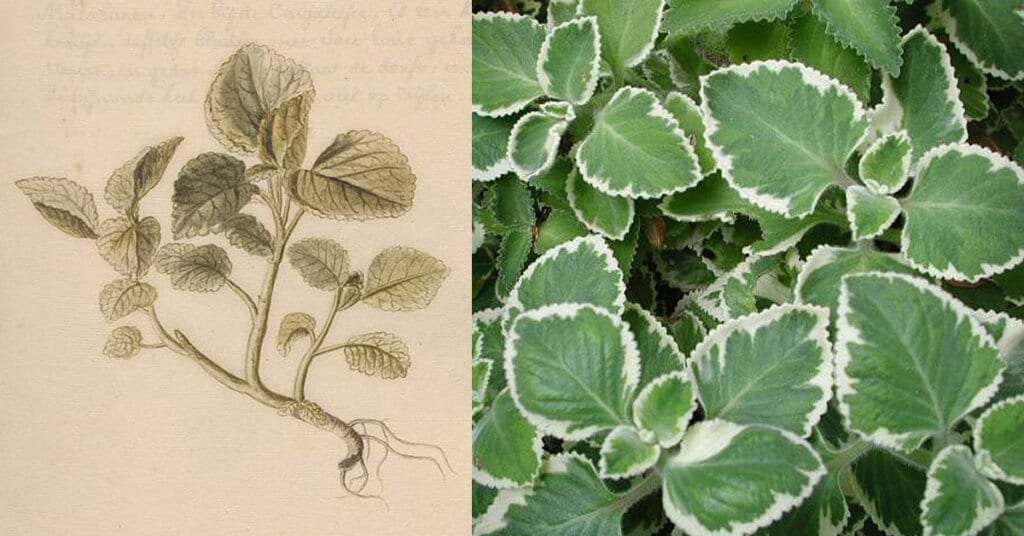
A semi-succulent perennial plant in the family Lamiaceae with a pungent oregano-like flavor and odor. Coleus amboinicus is considered to be native to parts of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and India, although it is widely cultivated and naturalized elsewhere in the tropics where it is used as a spice and ornamental plant. Common names in English include Indian borage, country borage, French thyme, Indian mint, Mexican mint, Cuban oregano, soup mint, Spanish thyme. The species epithet, amboinicus refers to Ambon Island, in Indonesia, where it was apparently encountered and described by João de Loureiro (1717 – 1791). [2]Wikipedia
Description
A member of the mint family Lamiaceae, Coleus amboinicus grows up to 1 m (3.3 ft) tall. The stem is fleshy, about 30–90 cm (12–35 in), either with long rigid hairs (hispidly villous) or densely covered with soft, short and erect hairs (tomentose). Old stems are smooth (glabrescent). [3]Wikipedia
Leaves are 5–7 cm (2.0–2.8 in) by 4–6 cm (1.6–2.4 in), fleshy, undivided (simple), broad, egg/oval-shaped with a tapering tip (ovate). The margins are coarsely crenate to dentate-crenate except in the base. They are thickly studded with hairs (pubescent), with the lower surface possessing the most numerous glandular hairs, giving a frosted appearance. The petiole is 2–4.5 cm (0.79–1.77 in). The aroma of the leaves can be described as a pungent combination of the aromas of oregano, thyme, and turpentine. The taste of the leaves is described as being similar to the one of oregano, but with a sharp mint-like flavor. [4]Wikipedia
Flowers are on a short stem (shortly pedicelled), pale purplish, in dense 10-20 (or more) flowered dense whorls (cymes), at distant intervals, in a long slender spike-like raceme. Rachis 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in), fleshy and pubescent. The bracts are broadly ovate, 3–4 cm (1.2–1.6 in) long, acute. The calyx is campanulate, 2–4 mm (0.079–0.157 in) long, hirsute and glandular, subequally 5-toothed, upper tooth broadly ovate-oblong, obtuse, abruptly acute, lateral and lower teeth acute. Corolla blue, curved and declinate, 8–12 mm (0.31–0.47 in) long, tube 3–4 mm (0.12–0.16 in) long. Trumpet-like widened; limb 2-lipped, upper lip short, erect, puberulent, lower lip long, concave. Filaments are fused below into a tube around the style. [5]Wikipedia
The seeds (nutlets) are smooth, pale-brown, roundish flattened, c. 0.7 by 0.5 mm (0.028 by 0.020 in). [6]Wikipedia
Distribution and habitat
Coleus amboinicus is native to Southern and Eastern Africa, from South Africa (KwaZulu-Natal) and Eswatini to Angola and Mozambique and north to Kenya and Tanzania, where it grows in woodland or coastal bush, on rocky slopes and loamy or sandy flats at low elevations. From Southern Africa it would have been carried by Arabs and other traders to Arabia, India and Southeast Asia along the Indian Ocean maritime trade routes. The plant also currently grows in mainland India. The plant was later brought to Europe, and then from Spain to the Americas, hence the name Spanish thyme. [7]Wikipedia
Research
In basic research, the effects of the essential oil were tested with other plant essential oils for possible use as a mosquito repellant. [8]Wikipedia
Uses
The leaves are strongly flavored. The herb is used as a substitute for oregano to mask the strong odors and flavors of fish, mutton, and goat. Fresh leaves are used to scent laundry and hair. It is also grown as an ornamental plant. [9]Wikipedia
Phytochemicals
The main chemical compounds found in the essential oil of Coleus amboinicus are carvacrol (28.65%), thymol (21.66%), α-humulene (9.67%), undecanal (8.29%), γ-terpinene (7.76%), p-cymene (6.46%), caryophyllene oxide (5.85%), α-terpineol (3.28%), and β-selinene (2.01%). [10]Wikipedia
Another analysis obtained thymol (41.3%), carvacrol (13.25%), 1,8-cineole (5.45%), eugenol (4.40%), caryophyllene (4.20%), terpinolene (3.75%), α-pinene (3.20%), β-pinene (2.50%), methyl eugenol (2.10%), and β-phellandrene (1.90%). The variations can be attributed to the methodology used in the extraction process, seasonal variations, soil type, climate, genetic and geographical variations of the plant. [11]Wikipedia
The information on this website has been compiled from reliable sources, such as reference works on medicinal plants. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment and Thaifoodmaster does not purport to provide any medical advice.
References