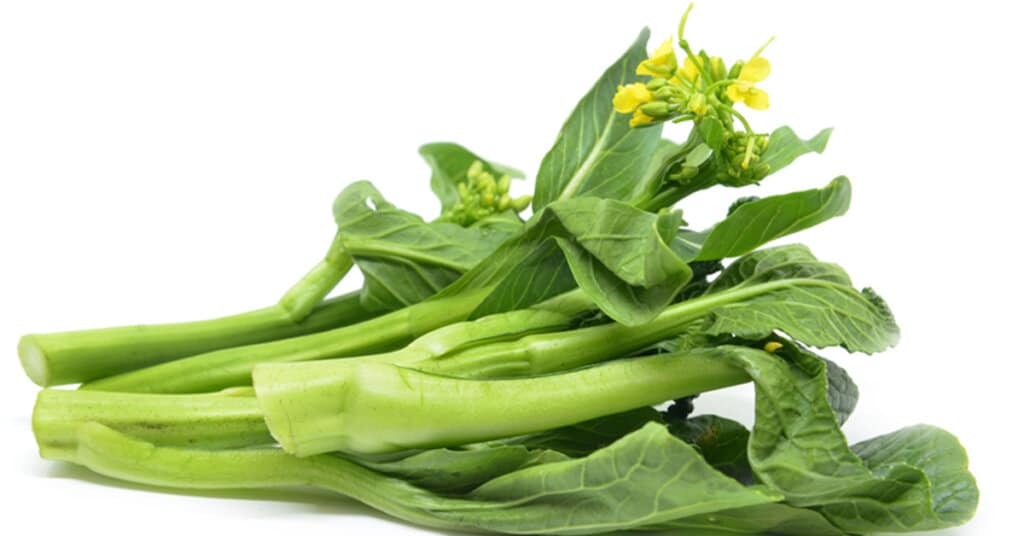
Other Names:
False pakchoi, ock pakchoi (USA), lowering white cabbage (UK), Pakchoi (FR)
Local Names:
ผักกวางตุ้ง (phak gwaang dtoong), ผักกาดเขียวกวางตุ้ง (phak gaat khiaao gwaang dtoong), ผักกาดฮ่องเต้ (phak gaat haawng dteh), ผักกวางตุ้งฮ่องเต้ (phak gwaang dtoong haawng dteh), กวางตุ้งไต้หวัน (gwaang dtoong dtai wan). Southern provinces: ผักกาดสายซิม (phak gaat saai sim).
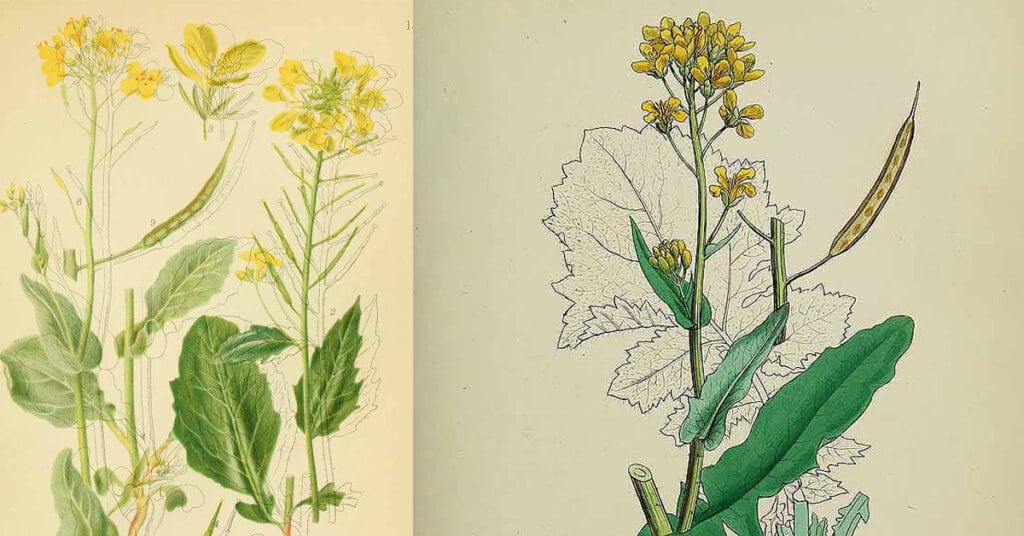
Brassica rapa is a plant species growing in various widely cultivated forms including the turnip (a root vegetable); napa cabbage, bomdong, bok choy, and rapini; and Brassica rapa subsp. oleifera, an oilseed which has many common names, including turnip rape, field mustard, bird’s rape, and keblock. [1]Wikipedia
The oil made from the seed is sometimes also called Canola Oil or Colza oil. The term rapeseed oil is a general term for oil from Brassica species that may not conform to Canola or Colza standards. Canola refers to three species of Brassica plants: Brassica rapa (Polish canola) is the less commonly grown, Brassica napus (Argentine canola), commonly grown in Canada and Brassica juncea (brown mustard) is a minor crop. [2]Wikipedia
History
The origin of B. rapa, both geographically and any surviving wild relatives, has been difficult to identify because it has been developed by humans into many types of vegetables, is now found in most parts of the world, and has returned to the wild many times as a feral plant. A study of genetic sequences from over 400 domesticated and feral B. rapa individuals, along with environmental modelling, has provided more information about the complex history. These indicate that the ancestral B. rapa probably originated 4000 to 6000 years ago in the Hindu Kush area of Central Asia, and had three sets of chromosomes. This provided the genetic potential for a diversity of form, flavour and growth requirements. Domestication has produced modern vegetables and oil-seed crops, all with two sets of chromosomes. [3]Wikipedia
Oilseed subspecies (oleifera) of Brassica rapa may have been domesticated several times from the Mediterranean to India, starting as early as 2000 BC. Edible turnips were possibly first cultivated in northern Europe, and were an important food in ancient Rome. The turnip then spread east to China, and reached Japan by 700 AD. There are descriptions of B. rapa vegetables in Indian and Chinese documents from around 1000 BC. [4]Wikipedia
In the 18th century the turnip and the oilseed-producing variants were seen as being different species by Carl Linnaeus who named them B. rapa and B. campestris. Twentieth-century taxonomists found that the plants were cross fertile and thus belonged to the same species. Since the turnip had been named first by Linnaeus, the name Brassica rapa was adopted. [5]Wikipedia
The information on this website has been compiled from reliable sources, such as reference works on medicinal plants. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment and Thaifoodmaster does not purport to provide any medical advice.

References